Module Overview
Once you have developed your plan proposal and worked out all the details with your applied behavioral analysis or in the case of this class, your instructor, its time to bring about positive change. Module 12 is short and sweet, but important. We will go over how to get started and what to do during your treatment phase.
Module Outline
- 12.1. The Treatment Phase
- 12.2. Record Keeping
- 12.3. Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns
Module Learning Outcomes
- Discuss the treatment phase of your behavior modification plan.
- Explain the importance of wellness and the eight dimensions.
- Implement your plan.
- Use the ABC chart and journal for record keeping.
- Outline your hopes and concerns about your project and clarify how self-instructions can aid with any doubts.
12.1. The Treatment Phase
Section Learning Objectives
- Define the treatment phase.
- Identify and explain the eight dimensions of wellness.
- Demonstrate how the dimensions relate to every behavior a person might desire to change.
Now that you have a behavior modification plan to change your target behavior for the good, it is time to implement the plan and see how it works. The treatment phase is when you employ all antecedent, behavior, and consequence-focused strategies. In the grand scheme of scientific research and specifically experiments, the treatment phase, but more so the strategies, are your IV or independent variable. Remember, this is the one that is manipulated. You have chosen certain strategies and decided to use them in a specific way which is the essence of manipulation. If you are doing a self-modification project in your class, consider that you and your classmates will have used antecedent manipulations and may have chosen to present a cue for the desirable behavior. Even if you and another student are trying to work out more and are using this strategy, you might decide to employ it in different ways. Maybe you will leave your clothes by your bed, but your classmate may leave the clothes in their bathroom. Both are cues to engage in the target, or desirable, behavior. Maybe instead the classmate uses their phone as a reminder to workout, assuming the phone is also not a temptation to engage in the undesirable behavior of surfing Facebook or playing a game. No matter what, manipulation is at work but so is measurement. Recall that your behavior is measured via your goals and behavior counts and is the dependent variable or DV.
Your treatment phase will last three weeks, though different instructors may make this time shorter or longer. To be able to really see if your strategies are working, you need two weeks at least. Though the designated treatment phase will end after at minimum two weeks, that is just for the purpose of having time to write your project up. Feel free to continue past this. The skills you learned in this class go well beyond this class. You will use these, or have strategies used on you such as prompting, reinforcement, and punishment procedures, all throughout life. So the applicability of the subject is enormous. Outside of that, if you have a true target behavior you want to establish or change, the impact can last the rest of your life and lead to better health and wellness. How so?
The Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) defines wellness as “being in good physical and mental health.” They add, “Remember that wellness is not the absence of illness or stress. You can still strive for wellness even if you are experiencing these challenges in your life.” Most people see wellness as just focused on the physical or mental. These are part of the picture, but definitely not the whole picture. SAMHSA proposes eight dimensions of wellness as follows (this information is directly from their website):
- Physical – Recognizing the need for physical activity, healthy foods, and sleep.
- Emotional – Coping effectively with life and creating satisfying relationships.
- Environmental – Good health by occupying pleasant, stimulating environments that support well-being
- Financial – Satisfaction with current and future financial situations
- Intellectual – Recognizing creative abilities and finding ways to expand knowledge and skills
- Occupational – Personal satisfaction and enrichment from one’s work
- Social – Developing a sense of connection, belonging, and a well-developed support system
- Spiritual – Expanding a sense of purpose and meaning in life
Okay. So who cares? Consider the following target behaviors students attempt to change for the better and which dimensions of wellness could be affected:
Table 12.1. Target Behavior and Impacted Dimensions of Wellness
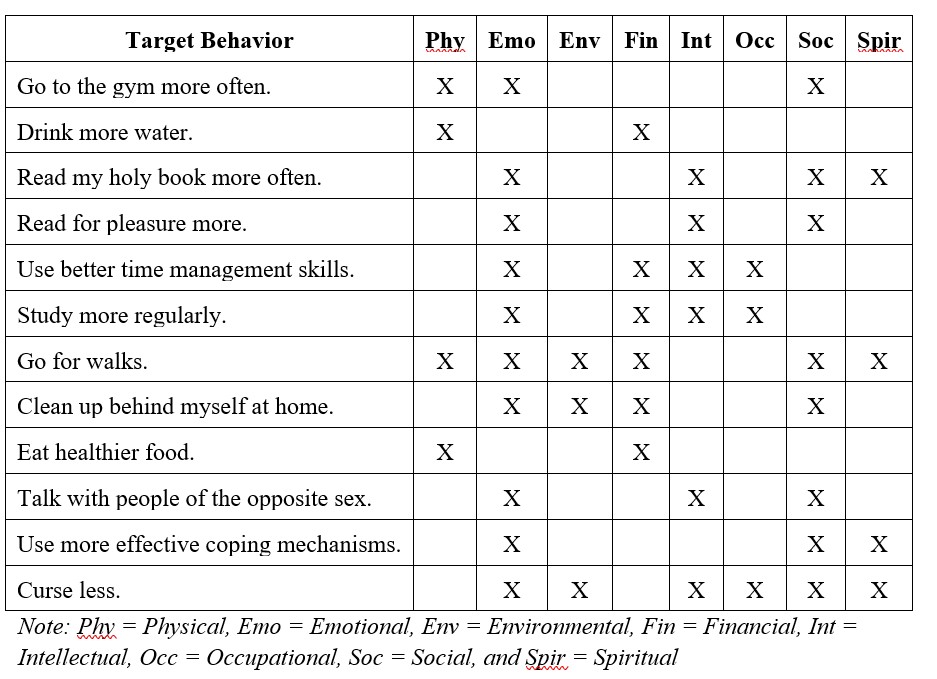
You could make a case for other dimensions on some of these, but I am sure the bigger issue is that you might be thinking how in the world could that dimension relate to that target behavior? I don’t wish to spend a lot of time on the 12 target behaviors I used as examples explaining why I selected these various dimensions of wellness, so I will just cover four. You can think critically about the other 8 behaviors, and others you might decide are worth changing.
- Go for walks – Physical is obvious. Emotional might be too but this is an opportunity to get away from life and destress. If you go for a walk in a park, you are communing with nature which is environmental and potentially spiritual. If you go with another person, you are working on social and while walking you could engage in a conversation of current issues which is intellectual. Financial is on the list because unlike going to the gym, walking outside is free.
- Read a holy book – This can help you find meaning and purpose in life which is spiritual or to discover another coping mechanism which is emotional. If you are in a Bible study group this is social and intellectual, and as for the latter, you will discuss what individual passages mean on a personal and general level.
- Cleaning up behind myself at home – If you are staying clean you save yourself needless stress of angry roommates which is emotional. Respecting your roommates and their wishes is social. A clean house is part of environmental wellness. Keeping clean means you guarantee yourself a place to live which ties into financial wellness, as having to find another place to live may cost you more money.
- Study more regularly – Emotional in regards to stress reduction. If you fail a class you have to pay to repeat it which impacts financial wellness. Intellectual in terms of mastering material related to your major. Better grades open up more doors when you start applying for jobs and so occupational wellness.
As you can see, you get quite a lot of bang for your buck when you bring about positive behavioral change. So let’s get started.
12.2. Record Keeping
Section Learning Objectives
- Use the ABC chart during treatment phase and keep a brief journal.
There is nothing to do here. Your plan has been decided. You just need to start it. So when do you this? Simply, follow the lead of your instructor or ABA specialist as to when they have decided the treatment phase will occur. Ideally start your plan the first day of the week as soon as you wake up. Personally commit to this start date and time before it arrives. This way you are motivated to see yourself change for the better. Also, you may need to physically manipulate your environment in a way consistent with the strategies you selected such as leaving clothes by your bed or taking a water bottle with you to school. Be sure this is all in place ahead of time. Follow your plan rules.
Be sure you use the ABC charts and journal that I have provided below to last the entire treatment phase. If you are not carrying them with you throughout the day, make sure you have your intermediary recording method in place such as downloading a needed app on your phone.
Note one major change in the treatment phase ABC charts that was not present during the baseline phase – the presence of a comment box at the bottom to serve as a journal entry for the day. You will want to record anything that is important to understanding either the complete failure, partial failure/success, or complete success of your plan. This qualitative data complements the quantitative data and really adds the level of understanding you may need to understand how your plan is going or went.
Figure 12.1: Sample ABC Chart and Journal
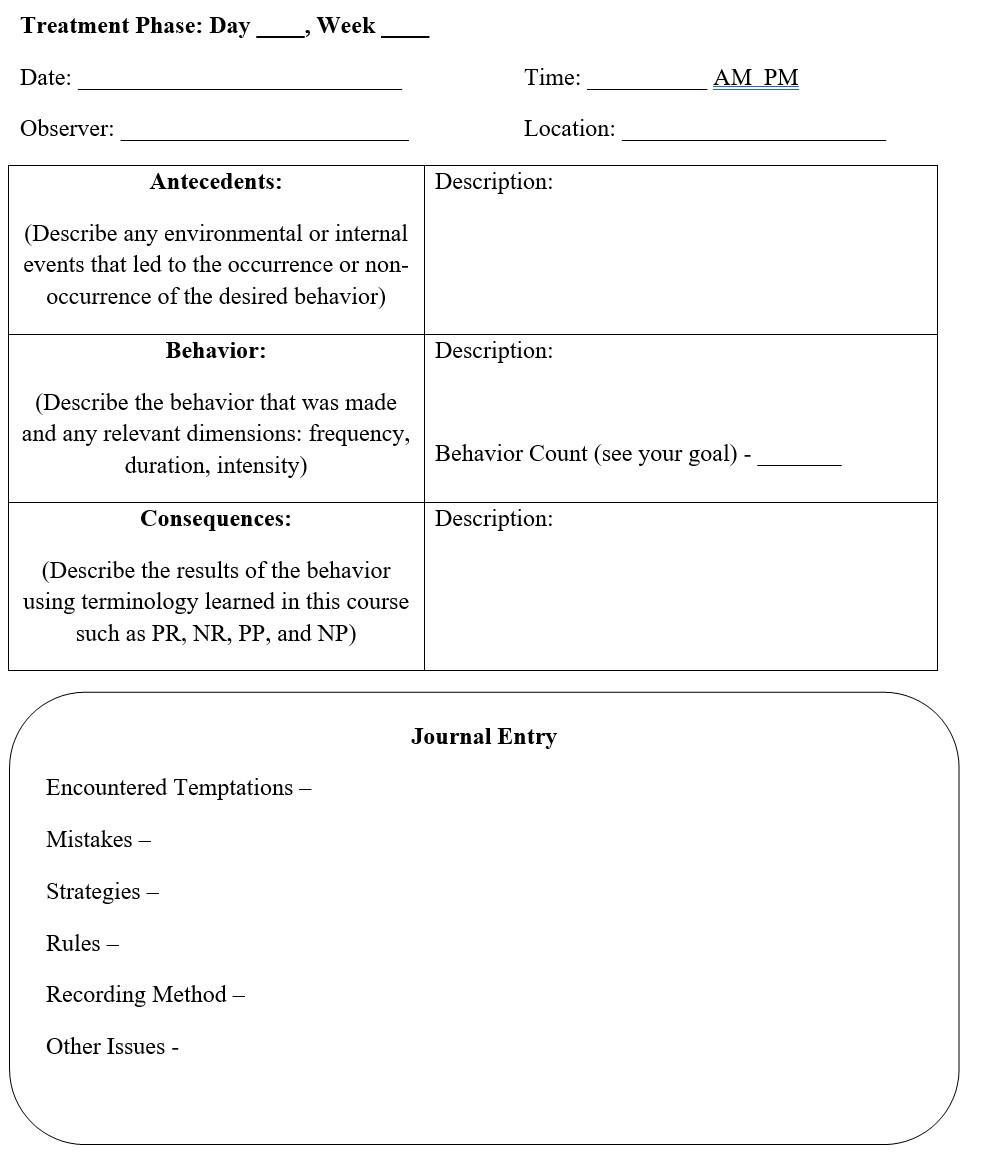
Your journal entry can include any information you feel is relevant. I included a few talking points such as which temptations were encountered and how you dealt with them, any mistakes you might have made, success of your strategies, clarity of your rules, effectiveness of your recording method and plan, and any other issues that may arise. Don’t wait to complete these daily journal entries as the passage of time will decay your memory and make completing them much more difficult. Plus, you may forget something relevant that can help explain your plan’s success or failure later. If there were no temptations or mistakes, or issues with the strategies or rules, just leave this blank. I would maybe note that there were no issues so you don’t wonder later if you simply forgot to make notes. Any information about the ABCs of behavior will go in the table above the journal, as well as a behavior count in the row for behavior. If you believe your behavioral definition is flawed, note it in both tables. Changing a definition while you are implementing a plan can be tricky so consult your instructor or ABA analyst for advice.
As a note, the process of recording the ABCs and what is working and what is not, will be more involved for some of you than others. Individuals with a plan involving increasing working out will only need to record once a day when they work out while someone tackling drinking water will likely have to record throughout the day as water is consumed. Bear this in mind but in the end, you all are reducing some problem behavior or increasing a desired one.
12.3. Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns
Section Learning Objectives
- Express your greatest hopes and concerns related to starting and implementing your behavior modification plan.
- Identify the psychological construct resulting from comparing your list of hopes and concerns with those of your classmates (done through a class activity).
- Produce a list of comforting words to help you deal with failures that might occur in your plan.
- Identify the psychological construct represented by these statements.
Note to Reader: To best make use of, and understand, what this section talks about, please see the Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns worksheet at the end of this module.
12.3.1. Hopes and Concerns
We all have a secret list of hopes about starting our plan and how it may turn out, but as well, we have concerns about what implementing the plan will mean for us. Take a minute to engage in introspection and address the two questions in Part 1 of the worksheet. Once you are finished with this, you will discover what your fellow classmates had to say. Use the table that follows to record some of their hopes and concerns and then compare their list with your own items. Are there similarities? Are there hopes or concerns that they expressed that apply to you as well? I will bet that you find more in common with your classmates than you do differences with them. Often, in the course of behavioral change, we feel alone and that our experience is unique. You are not alone, and it is not unique. As you can see, others feel like you do. This shows the psychological construct of social belongingness.
12.3.2. Thinking about Plan Failure(s)
Now proceed to Part 2 and consider what you will do if your plan does not work as expected and how it may make you feel. Be realistic when answering this as many plans hit roadblocks along the way. These will often just slow down your success; not completely derail the plan though this does happen at times (See Module 13 for a discussion of what to do). Once you have done this, move to Part 3. Write a few, kind, understanding words of comfort to help you deal with this reality of plan failure or just partial failure. These effectively can serve as additional self-instructions (remember, an antecedent focused strategy) to use when times are tough and not going as you expected. By doing some planning now, you may stave off complete plan failure. These statements/self-instructions help you to show yourself self-compassion (the psychological construct) and not to beat yourself up over setbacks on your road to success.
12.3.3. Final Thoughts
These two exercises are important and as noted, are in keeping with sound and important psychological constructs – first, social belongingness or the idea that you are not alone and others feel like you do and second, self-compassion or the idea that you excuse yourself from guilt over temporary setbacks when the plan proves more challenging than you thought it would be to achieve. Keep both ideas in mind as they can serve as additional motivators for engaging in behavioral change, and in keeping in the pros and cons analysis, self-efficacy assessment, accounting of your core values, and identification of a growth mindset (or compensating for a fixed mindset) discussed in Module 3.
The worksheet follows this section.
Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns Worksheet
Click here to access the Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns Worksheet in MS Word format – Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns Worksheet
Click here to access the Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns Worksheet in PDF format – Treatment Phase Hopes and Concerns Worksheet
Module Recap
You are now ready to rock and roll. This project is all about you and changing a behavior you are excited about. Likely, you will be successful at least in part. Some of your strategies or rules may not work out and that is fine. Heck, your whole plan may be a disaster. Though I truly hope this is not the case, taking detailed notes during the treatment phase will help you to figure out why you succeeded or failed. And thinking about what you hope to achieve and what concerns you have about your plan’s progression and eventual success can go a long way to making success likely, even if delayed. Remember, others feel like you do about this effort to engage in behavioral change. You are not alone. Good luck!
4th edition (4.10)
