Opening Case: China in Africa
Foreign companies have been doing business in Africa for centuries. Much of the trade history of past centuries has been colored by European colonial powers promoting and preserving their economic interests throughout the African continent.1 After World War II and since independence for many African nations, the continent has not fared as well as other former colonial countries in Asia. Africa remains a continent plagued by a continued combination of factors, including competing colonial political and economic interests; poor and corrupt local leadership; war, famine, and disease; and a chronic shortage of resources, infrastructure, and political, economic, and social will.2 And yet, through the bleak assessments, progress is emerging, led in large part by the successful emergence of a free and locally powerful South Africa. The continent generates a lot of interest on both the corporate and humanitarian levels, as well as from other countries. In particular in the past decade, Africa has caught the interest of the world’s second largest economy, China.3
At home, over the past few decades, China has undergone its own miracle, managing to move hundreds of millions of its people out of poverty by combining state intervention with economic incentives to attract private investment. Today, China is involved in economic engagement, bringing its success story to the continent of Africa. As professor and author Deborah Brautigam notes, China’s “current experiment in Africa mixes a hard-nosed but clear-eyed self-interest with the lessons of China’s own successful development and of decades of its failed aid projects in Africa.” 4
According to CNN, “China has increasingly turned to resource-rich Africa as China’s booming economy has demanded more and more oil and raw materials.”5 Trade between the African continent and China reached $106.8 billion in 2008, and over the past decade, Chinese investments and the country’s development aid to Africa have been increasing steadily.“China-Africa Trade up 45 percent in 2008 to $107 Billion,” 6 “Chinese activities in Africa are highly diverse, ranging from government to government relations and large state owned companies (SOE) investing in Africa financed by China’s policy banks, to private entrepreneurs entering African countries at their own initiative to pursue commercial activities.”7
Since 2004, eager for access to resources, oil, diamonds, minerals, and commodities, China has entered into arrangements with resource-rich countries in Africa for a total of nearly $14 billion in resource deals alone. In one example with Angola, China provided loans to the country secured by oil. With this investment, Angola hired Chinese companies to build much-needed roads, railways, hospitals, schools, and water systems. Similarly, China provided nearby Nigeria with oil-backed loans to finance projects that use gas to generate electricity. In the Republic of the Congo, Chinese teams are building a hydropower project funded by a Chinese government loan, which will be repaid in oil. In Ghana, a Chinese government loan will be repaid in cocoa beans.8
The Export-Import Bank of China (Ex-Im Bank of China) has funded and has provided these loans at market rates, rather than as foreign aid. While these loans certainly promote development, the risk for the local countries is that the Chinese bids to provide the work aren’t competitive. Furthermore, the benefit to local workers may be diminished as Chinese companies bring in some of their own workers, keeping local wages and working standards low.
In 2007, the UNCTAD (United Nations Conference on Trade and Development) Press Office noted the following:
Over the past few years, China has become one of Africa´s important partners for trade and economic cooperation. Trade (exports and imports) between Africa and China increased from US$11 billion in 2000 to US$56 billion in 2006….with Chinese companies present in 48 African countries, although Africa still accounts for only 3 percent of China´s outward FDI [foreign direct investment]. A few African countries have attracted the bulk of China´s FDI in Africa: Sudan is the largest recipient (and the 9th largest recipient of Chinese FDI worldwide), followed by Algeria (18th) and Zambia (19th).9
Observers note that African governments can learn from the development history of China and many Asian countries, which now enjoy high economic growth and upgraded industrial activity. These Asian countries made strategic investments in education and infrastructure that were crucial not only for promoting economic development in general but also for attracting and benefiting from efficiency-seeking and export-oriented FDI.10
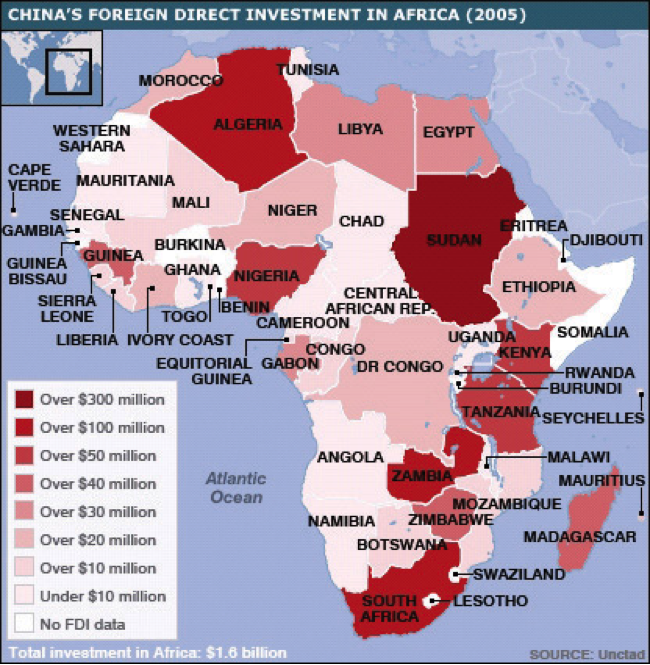
Source: “China in Africa: Developing Ties,” BBC News, last updated November 26, 2007, accessed June 3, 2011, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7086777.stm.
Criticized by some and applauded by others, it’s clear that China’s investment is encouraging development in Africa. China is accused by some of ignoring human rights crises in the continent and doing business with repressive regimes. China’s success in Africa is due in large part to the local political environment in each country, where either one or a small handful of leaders often control the power and decision making. While the countries often open bids to many foreign investors, Chinese firms are able to provide low-cost options thanks in large part to their government’s project support. The ability to forge a government-level partnership has enabled Chinese businesses to have long-term investment perspectives in the region. China even hosted a summit in 2006 for African leaders, pledging to increase trade, investment, and aid over the coming decade.11 The 2008 global recession has led China to be more selective in its African investments, looking for good deals as well as political stability in target countries. Nevertheless, whether to access the region’s rich resources or develop local markets for Chinese goods and services, China intends to be a key foreign investor in Africa for the foreseeable future.12
Learning Objectives
- Understand international trade.
- Compare and contrast different trade theories.
- Determine which international trade theory is most relevant today and how it continues to evolve.
What Is International Trade?
International trade theories are simply different theories to explain international trade. Trade is the concept of exchanging goods and services between two people or entities. International trade is then the concept of this exchange between people or entities in two different countries.
People or entities trade because they believe that they benefit from the exchange. They may need or want the goods or services. While at the surface, this many sound very simple, there is a great deal of theory, policy, and business strategy that constitutes international trade.
| “Around 5,200 years ago, Uruk, in southern Mesopotamia, was probably the first city the world had ever seen, housing more than 50,000 people within its six miles of wall. Uruk, its agriculture made prosperous by sophisticated irrigation canals, was home to the first class of middlemen, trade intermediaries…A cooperative trade network…set the pattern that would endure for the next 6,000 years.” Matt Ridley, “Humans: Why They Triumphed,” Wall Street Journal, May 22, 2010, accessed December 20, 2010, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703691804575254533386933138.html. |
Mercantilism
Developed in the sixteenth century, mercantilism was one of the earliest efforts to develop an economic theory. This theory stated that a country’s wealth was determined by the amount of its gold and silver holdings. In it’s simplest sense, mercantilists believed that a country should increase its holdings of gold and silver by promoting exports and discouraging imports. In other words, if people in other countries buy more from you (exports) than they sell to you (imports), then they have to pay you the difference in gold and silver. The objective of each country was to have a trade surplus, or a situation where the value of exports are greater than the value of imports, and to avoid a trade deficit, or a situation where the value of imports is greater than the value of exports.
A closer look at world history from the 1500s to the late 1800s helps explain why mercantilism flourished. The 1500s marked the rise of new nation-states, whose rulers wanted to strengthen their nations by building larger armies and national institutions. By increasing exports and trade, these rulers were able to amass more gold and wealth for their countries. One way that many of these new nations promoted exports was to impose restrictions on imports. This strategy is called protectionism and is still used today.
Nations expanded their wealth by using their colonies around the world in an effort to control more trade and amass more riches. The British colonial empire was one of the more successful examples; it sought to increase its wealth by using raw materials from places ranging from what are now the Americas and India. France, the Netherlands, Portugal, and Spain were also successful in building large colonial empires that generated extensive wealth for their governing nations.
Although mercantilism is one of the oldest trade theories, it remains part of modern thinking. Countries such as Japan, China, Singapore, Taiwan, and even Germany still favor exports and discourage imports through a form of neo-mercantilism in which the countries promote a combination of protectionist policies and restrictions and domestic-industry subsidies. Nearly every country, at one point or another, has implemented some form of protectionist policy to guard key industries in its economy. While export-oriented companies usually support protectionist policies that favor their industries or firms, other companies and consumers are hurt by protectionism. Taxpayers pay for government subsidies of select exports in the form of higher taxes. Import restrictions lead to higher prices for consumers, who pay more for foreign-made goods or services. Free-trade advocates highlight how free trade benefits all members of the global community, while mercantilism’s protectionist policies only benefit select industries, at the expense of both consumers and other companies, within and outside of the industry.
Absolute Advantage
In 1776, Adam Smith questioned the leading mercantile theory of the time in The Wealth of Nations.Adam Smith, An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (London: W. Strahan and T. Cadell, 1776). Recent versions have been edited by scholars and economists. Smith offered a new trade theory called absolute advantage, which focused on the ability of a country to produce a good more efficiently than another nation. Smith reasoned that trade between countries shouldn’t be regulated or restricted by government policy or intervention. He stated that trade should flow naturally according to market forces. In a hypothetical two-country world, if Country A could produce a good cheaper or faster (or both) than Country B, then Country A had the advantage and could focus on specializing on producing that good. Similarly, if Country B was better at producing another good, it could focus on specialization as well. By specialization, countries would generate efficiencies, because their labor force would become more skilled by doing the same tasks. Production would also become more efficient, because there would be an incentive to create faster and better production methods to increase the specialization.
Smith’s theory reasoned that with increased efficiencies, people in both countries would benefit and trade should be encouraged. His theory stated that a nation’s wealth shouldn’t be judged by how much gold and silver it had but rather by the living standards of its people.
Comparative Advantage
The challenge to the absolute advantage theory was that some countries may be better at producing both goods and, therefore, have an advantage in many areas. In contrast, another country may not have any useful absolute advantages. To answer this challenge, David Ricardo, an English economist, introduced the theory of comparative advantage in 1817. Ricardo reasoned that even if Country A had the absolute advantage in the production of both products, specialization and trade could still occur between two countries.
Comparative advantage occurs when a country cannot produce a product more efficiently than the other country; however, it can produce that product better and more efficiently than it does other goods. The difference between these two theories is subtle. Comparative advantage focuses on the relative productivity differences, whereas absolute advantage looks at the absolute productivity.
Let’s look at a simplified hypothetical example to illustrate the subtle difference between these principles. Miranda is a Wall Street lawyer who charges $500 per hour for her legal services. It turns out that Miranda can also type faster than the administrative assistants in her office, who are paid $40 per hour. Even though Miranda clearly has the absolute advantage in both skill sets, should she do both jobs? No. For every hour Miranda decides to type instead of do legal work, she would be giving up $460 in income. Her productivity and income will be highest if she specializes in the higher-paid legal services and hires the most qualified administrative assistant, who can type fast, although a little slower than Miranda. By having both Miranda and her assistant concentrate on their respective tasks, their overall productivity as a team is higher. This is comparative advantage. A person or a country will specialize in doing what they do relatively better. In reality, the world economy is more complex and consists of more than two countries and products. Barriers to trade may exist, and goods must be transported, stored, and distributed. However, this simplistic example demonstrates the basis of the comparative advantage theory.
Modern or Firm-Based Trade Theories
In contrast to classical, country-based trade theories, the category of modern, firm-based theories emerged after World War II and was developed in large part by business school professors, not economists. The firm-based theories evolved with the growth of the multinational company (MNC). The country-based theories couldn’t adequately address the expansion of either MNCs or intraindustry trade, which refers to trade between two countries of goods produced in the same industry. For example, Japan exports Toyota vehicles to Germany and imports Mercedes-Benz automobiles from Germany.
Unlike the country-based theories, firm-based theories incorporate other product and service factors, including brand and customer loyalty, technology, and quality, into the understanding of trade flows.
Country Similarity Theory
Swedish economist Steffan Linder developed the country similarity theory in 1961, as he tried to explain the concept of intraindustry trade. Linder’s theory proposed that consumers in countries that are in the same or similar stage of development would have similar preferences. In this firm-based theory, Linder suggested that companies first produce for domestic consumption. When they explore exporting, the companies often find that markets that look similar to their domestic one, in terms of customer preferences, offer the most potential for success. Linder’s country similarity theory then states that most trade in manufactured goods will be between countries with similar per capita incomes, and intraindustry trade will be common. This theory is often most useful in understanding trade in goods where brand names and product reputations are important factors in the buyers’ decision-making and purchasing processes.
Product Life Cycle Theory
Raymond Vernon, a Harvard Business School professor, developed the product life cycle theory in the 1960s. The theory, originating in the field of marketing, stated that a product life cycle has three distinct stages: (1) new product, (2) maturing product, and (3) standardized product. The theory assumed that production of the new product will occur completely in the home country of its innovation. In the 1960s this was a useful theory to explain the manufacturing success of the United States. US manufacturing was the globally dominant producer in many industries after World War II.
It has also been used to describe how the personal computer (PC) went through its product cycle. The PC was a new product in the 1970s and developed into a mature product during the 1980s and 1990s. Today, the PC is in the standardized product stage, and the majority of manufacturing and production process is done in low-cost countries in Asia and Mexico.
The product life cycle theory has been less able to explain current trade patterns where innovation and manufacturing occur around the world. For example, global companies even conduct research and development in developing markets where highly skilled labor and facilities are usually cheaper. Even though research and development is typically associated with the first or new product stage and therefore completed in the home country, these developing or emerging-market countries, such as India and China, offer both highly skilled labor and new research facilities at a substantial cost advantage for global firms.
Global Strategic Rivalry Theory
Global strategic rivalry theory emerged in the 1980s and was based on the work of economists Paul Krugman and Kelvin Lancaster. Their theory focused on MNCs and their efforts to gain a competitive advantage against other global firms in their industry. Firms will encounter global competition in their industries and in order to prosper, they must develop competitive advantages. The critical ways that firms can obtain a sustainable competitive advantage are called the barriers to entry for that industry. The barriers to entry refer to the obstacles a new firm may face when trying to enter into an industry or new market. The barriers to entry that corporations may seek to optimize include:
- research and development,
- the ownership of intellectual property rights,
- economies of scale,
- unique business processes or methods as well as extensive experience in the industry, and
- the control of resources or favorable access to raw materials.
Porter’s National Competitive Advantage Theory
In the continuing evolution of international trade theories, Michael Porter of Harvard Business School developed a new model to explain national competitive advantage in 1990. Porter’s theory stated that a nation’s competitiveness in an industry depends on the capacity of the industry to innovate and upgrade. His theory focused on explaining why some nations are more competitive in certain industries. To explain his theory, Porter identified four determinants that he linked together. The four determinants are (1) local market resources and capabilities, (2) local market demand conditions, (3) local suppliers and complementary industries, and (4) local firm characteristics.
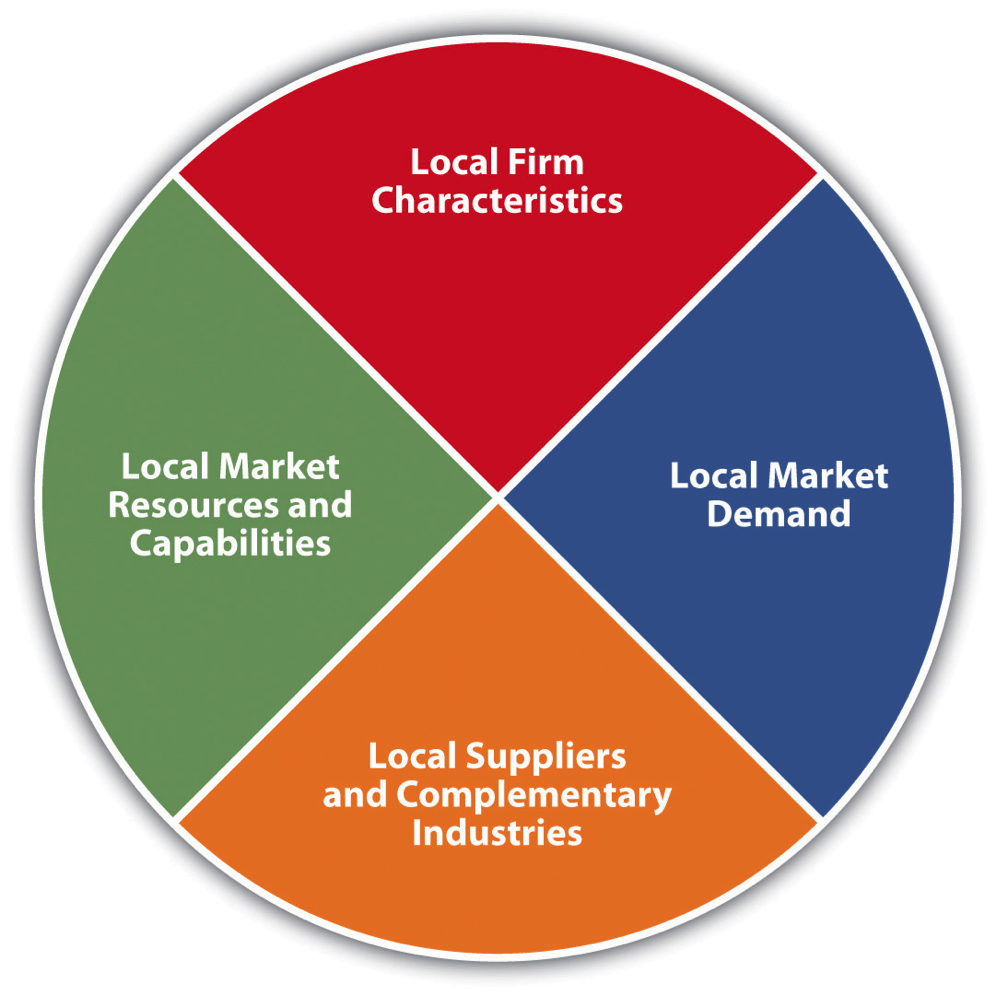
- Local market resources and capabilities (factor conditions). Porter recognized the value of the factor proportions theory, which considers a nation’s resources (e.g., natural resources and available labor) as key factors in determining what products a country will import or export. Porter added to these basic factors a new list of advanced factors, which he defined as skilled labor, investments in education, technology, and infrastructure. He perceived these advanced factors as providing a country with a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Local market demand conditions. Porter believed that a sophisticated home market is critical to ensuring ongoing innovation, thereby creating a sustainable competitive advantage. Companies whose domestic markets are sophisticated, trendsetting, and demanding forces continuous innovation and the development of new products and technologies. Many sources credit the demanding US consumer with forcing US software companies to continuously innovate, thus creating a sustainable competitive advantage in software products and services.
- Local suppliers and complementary industries. To remain competitive, large global firms benefit from having strong, efficient supporting and related industries to provide the inputs required by the industry. Certain industries cluster geographically, which provides efficiencies and productivity.
- Local firm characteristics. Local firm characteristics include firm strategy, industry structure, and industry rivalry. Local strategy affects a firm’s competitiveness. A healthy level of rivalry between local firms will spur innovation and competitiveness.
In addition to the four determinants of the diamond, Porter also noted that government and chance play a part in the national competitiveness of industries. Governments can, by their actions and policies, increase the competitiveness of firms and occasionally entire industries.
Porter’s theory, along with the other modern, firm-based theories, offers an interesting interpretation of international trade trends. Nevertheless, they remain relatively new and minimally tested theories.
REFERENCES
1. Martin Meredith, The Fate of Africa (New York: Public Affairs, 2005).
2. “Why Africa Is Poor: Ghana Beats Up on Its Biggest Foreign Investors,” Wall Street Journal, February 18, 2010, accessed February 16, 2011, http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704804204575069511746613890.html.
3. Andrew Rice, “Why Is Africa Still Poor?,” The Nation, October 24, 2005, accessed December 20, 2010, http://www.thenation.com/article/why-africa-still-poor?page=0,1.
4. Deborah Brautigam, “Africa’s Eastern Promise: What the West Can Learn from Chinese Investment in Africa,” Foreign Affairs, January 5, 2010, accessed December 20, 2010, http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/65916/deborah-brautigam/africa%E2%80%99s-eastern-promise.
5. “China: Trade with Africa on Track to New Record,” CNN, October 15, 2010, accessed April 23, 2011, http://articles.cnn.com/2010-10-15/world/china.africa.trade_1_china-and-africa-link-trade-largest-trade-partner?_s=PM:WORLD.
6. China Daily, February 11, 2009, accessed April 23, 2011, http://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2009-02/11/content_7467460.htm.
7. Tracy Hon, Johanna Jansson, Garth Shelton, Liu Haifang, Christopher Burke, and Carine Kiala, Evaluating China’s FOCAC Commitments to Africa and Mapping the Way Ahead(Stellenbosch, South Africa: Centre for Chinese Studies, University of Stellenbosch, 2010), 1, accessed December 20, 2010, http://www.ccs.org.za/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/ENGLISH-Evaluating-Chinas-FOCAC-commitments-to-Africa-2010.pdf.
8. Deborah Brautigam, “Africa’s Eastern Promise: What the West Can Learn from Chinese Investment in Africa,” Foreign Affairs, January 5, 2010, accessed December 20, 2010, http://www.foreignaffairs.com/articles/65916/deborah-brautigam/africa%E2%80%99s-eastern-promise.
9. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, “Asian Foreign Direct Investment in Africa: United Nations Report Points to a New Era of Cooperation among Developing Countries,” press release, March 27, 2007, accessed December 20, 2010, http://www.unctad.org/Templates/Webflyer.asp?docID=8172&intItemID=3971&lang=1.
10. United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, “Foreign Direct Investment in Africa Remains Buoyant, Sustained by Interest in Natural Resources,” press release, September 29, 2005, accessed December 20, 2010, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7086777.stm.
11. “Summit Shows China’s Africa Clout,” BBC News, November 6, 2006, accessed December 20, 2010, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/6120500.stm.
12. “China in Africa: Developing Ties,” BBC News, November 26, 2007, accessed December 20, 2010, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/7086777.stm.
The above content was adapted under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work’s original creator or licensor.

I would like to thank Andy Schmitz for his work in maintaining and improving the HTML versions of these textbooks. This textbook is adapted from his HTML version, and his project can be found here.
